Consider the following triangle:
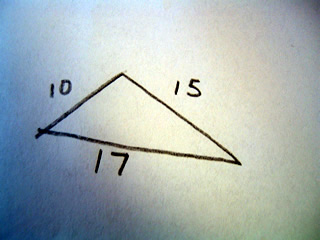
There are no right angles in the triangle, so therefore we must use Heron's forumla which first defines a variable s
s=1/2(a+b+c) where a,b,c each represent the length of a side.
then the area of the triangle is equal to
sqrt(s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c))
For the example we see that s=21
and the area is equal to
sqrt(21(21-10)(21-15)(21-17))
=
sqrt(21*11*6*4)=sqrt(5,544)=~74.46 which is the area of the triangle.
How do we prove Herons formula? Consider the triangle:
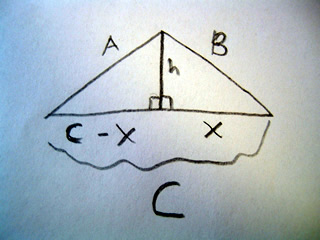
Here we have taken a triangle with no right angles, and cut a line so that we create two right triangles, and two new lengths at the base: x, and C-x. Now we need to solve for two unknown values x and h. We will solve for x first.
We can use pythagorean theorem to create equations for our new values, we see we have:
x2 + h2 = B2
and
(c-x)2 + h2 = A2
=
C2 - 2cx + x2+ h2 = A2
We know that B= x2+h2 so we substitute that in to the equation above and get
C2 - 2cx + B2 = A2
Now we can solve for x!
x= (A2 - B2 - C2) / - 2c
Now we have x we can plug it back in to the equation
x2 + h2 = B2
thus
h = sqrt(B2 - (A2 - B2 - C2) / - 2c)2)
Now, we know our base is equal to C and our height is equal to h, if we substitute these two values into the formula for the area of a triangle we get
(1/2)*b*h = 1/2*C2*sqrt(B2 - (A2 - B2 - C2) / - 2c)2)
That is a complicated formula, so Heron found that you could define a term
s = (1/2)*( A + B + C) and then found the area formula could become a simpler
sqrt(s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c))
If you plug s in to the area formula above you will find the result we saw above:
1/2*C2*sqrt(B2 - (A2 - B2 - C2) / - 2c)2)
which is the area of the triangle.




No comments:
Post a Comment